Main Page
Contents
A Blueprint and Implementation of a Public Data Ecosystem
Overview
The open data movement is gaining more momentum and is based on the assumption that more intensive and creative use of information and technology can improve policy-making and generate new forms of public value. Making data available for public use promotes transparency and accountability, economic development and expanded networks for knowledge creation. Past efforts in making data public has resulted in data being published in an ad-hoc manner, often through grass-roots efforts, with little consideration of access management, accountability or analytics. Consumers of public data want assurance that the data collection, management, access and dissemination practices used result in data provided that is valid, sufficient and appropriate for policy analysis or any other use. Data publishers must adhere to lifecycle processes in order to assure that the data accurate but is also fit for use considering both subjective perceptions and objective assessments which will have a bearing on the extent to which users are willing and able to use information. A systematic approach with an enterprise lifecycle perspective must be used to enable the full potential of open data. The most effective open data ecosystem produces benefits for the data consumer and the data provider but requires a structured, governed approach for supporting open data use. A civic effort in Minnesota has created a blueprint that addresses the strategy, design, deployment, operation and continual improvement of a public storefront to publish, discover, govern and manage publicly available data.
Summary: There are many social and economic benefits to making data available for public use, including transparency, accountability, economic development, and knowledge creation. The most effective system for publishing and delivering data requires a structured, governed approach designed from a lifecycle perspective for supporting data use.
Business Value and Return on Investment
The business value and return on investment of making public data available cannot be quantified in quantitative terms. A business makes decisions on the basis of quantifiable information that is used to develop a return on investment (ROI). If the ROI is within range of investment criteria, the decision to invest is easier to make. When it comes to making data open, the question for the government domain to answer is what is the cost of doing so and what is the expected business value since ROI cannot be determined in quantifiable terms. The value proposition of open data is associated with: 1) transparency and accountability, 2) economic development and smart disclosure, and 3) expanded policy networks for knowledge creation. A McKinsey report [1] expands on an important topic contained in a prior report[2] by McKinsey, which suggests that government can promote open data, and participates in over $3 trillion in economic value. Value creation can be enabled through promoting better decision making (more information results in better decisions), stimulating development of new products and services, and increasing transparency and improving accountability. Alex Howard[3] has discussed how open government promotes transparency and accountability, which is at the core of how government is thought about. When budgets are constrained, government officials question the value of each spending decision. Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, has said that increased transparency into a state’s finances and services directly relates to the willingness of businesses and other nations to invest in that government entity. The business value of open government is not always clear especially with respect to investment or outcomes. “Reactive” or “proactive” disclosure of information will affect the proliferation of data made available through public means. Reactive disclosure means that a question needs to be asked before an answer is given[4] while proactive disclosure is the release of information before it is requested. Open data policies and laws provide an opportunity not just to update and improve access to information that is already available but to specify that new data sets and records be published in a proactive manner hence influencing the use of data for public and business decisions. These open data efforts must be funded, however, and compete for budget dollars that may have greater public benefit than just simply the release of publicly available open data.
The challenges with releasing public data, in order to capitalize on perceived business value, require that effort be put into a comprehensive effort to manage, govern and make available public information and that a more systematic and structured approach should be considered in order to realize the potential business value of making public data available. The process of cleaning and preparing data to be published has returns for workers inside government itself and should be considered. A McKinsey[5] report indicates that government workers spend 19% of their time looking for information. The process of opening up public data clearly has benefits (and business value) for both external and internal users of this data.
What is the business value for a government domain to spend resources on opening up public data? There will be value for constituents (individual and commercial) who make use of the data to promote public or societal awareness and who develop commercial applications that are used for commercial purposes. The value to the government entity making the data available can have political, societal, and economic benefits. Users of the data can be important indicators of business activity and provide analytics to government entities to gain more insight into potential future economic value.
What data is made available and how to make it available are important parameters that need to be addressed in any public data initiative. In this sense, it is worthwhile to look at the delivery of open data to public consumers as a lifecycle process where data creation, data quality, data availability and data governance are key to assuring users that a rigorous enterprise approach to delivering data is in place making them more comfortable with the use and long term availability of the data.
Summary: There is great value generated by making public data available; in the U.S there is an estimated annual economic benefit of $1.1 trillion, due in part to increased efficiency and development of new products and services. Benefits can be difficult if not impossible to quantify directly as a return on investment and instead are better visualized as a value-add to constituents, governments, and companies; additionally, changing existing systems that are staff-time intensive (such as Data Practices Act requests) can reduce costs.
Government Domains
Governments collect or generate much data for their own purposes or from their own operations. If governments did not gain a net benefit from collecting and using data, they would not collect it to begin with. The U.S. Federal government has taken a lead in making open data available to the public. It recognizes information as a valuable national resource and a strategic asset to the Federal Government, its partners and the public. Its stated goals are to manage information as an asset throughout its life cycle to promote openness and interoperability and properly safeguard systems and information. Managing government information as an asset is expected to increase operational efficiencies, reduce costs, improve services, support mission needs, safeguard personal information and increase public access to valuable government information[6]. For example, the Federal Government website, data.gov, currently (September, 2014) has 108,498 data sets available on the data.gov portal.
The Federal Government has more resources available to it to invest in the development and delivery of an open data portal. Any government domain has the ability to gain value from making public data open and available but may not have the financial resources to invest in the infrastructure resources to make it available. To that extent, it is likely that smaller government domains may need to take advantage of larger domains that do have the ability to invest in open data initiatives.
All government domains, including federal, state, regional, county and city governments, should consider making their data available to the public. Because of the initial costs of making data available, not all entities will be able to make their data available. Funding may not be available at all because of the initial costs of a portal that will make the open data available to the public. To reduce the costs of providing open data to the public, small governments (e.g., small cities) could mutualize their expenses with other smaller entities or rely on other larger government infrastructure provided to share public data.
Summary: Governments can capture many benefits by making their data open, including: increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved services, support of their mission, and safeguarding of systems and information. It should be acknowledged that financial resources will be required to make data openly available, but a systematic view of costs for the existing system should be considered along with estimates of these benefits to the government and its constituents.
Stakeholders
There is general agreement among researchers that the public sector is complex and involves a variety of stakeholders [7]. Chircu[8] has shown that e-government projects are characterized by many stakeholders with multiple value dimensions (financial, social and political) but argues that few government studies adopt a multi-dimensional perspective incorporating all value dimensions and relevant stakeholders. Most studies in open data address the high level stakeholders, i.e., “the government”, “businesses” and “the public” as stakeholders. Identification of the stakeholders associated with a government open data initiative is important in order to determine costs and benefits. The benefits need to be addressed from a technical implementation perspective since there will be functions to be provided (through electronic means) in order to satisfy the information needs of the needs of the stakeholder and the cost of providing such information.
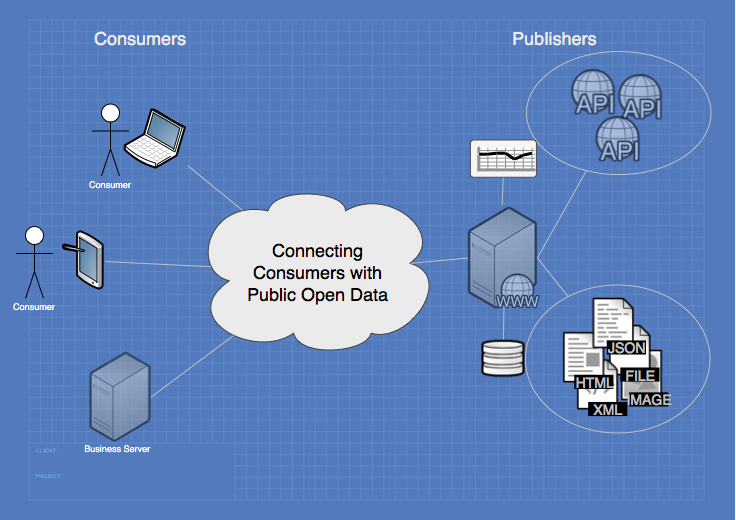
A stakeholder model for a public data ecosystem has been defined and is listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Public Data Ecosystem Stakeholders
The stakeholder model is used to determine information needs and technical infrastructure requirements for functions provided or managed by the respective stakeholder.
Summary: The stakeholder model is used to determine information needs and technical infrastructure requirements for functions provided or managed by the respective stakeholder.
Business Models
The exploration of potential business models around government open data initiatives aims to mitigate the risk of using public data when government funding is cut resulting in a reduced level of service to the consumers of public data. Reliance on the continual funding of the government entity providing the data is directly related to the perceived value that government is realizing from providing such public data. More importantly, an open data initiative may never get off the ground because of the lack of funding by the government entity. Even when funding is made available, it may not be at the levels required to get an open data initiative up and running. An analysis of potential public-private business models provides some reasonable alternatives that a government entity could adopt in order to deliver open data. Public and private sector organizations can learn from each other: 1) the private sector’s delivery model is motivated by profit gains, and 2) the public sector’s operating models are focused on well-documented quality measures and the risks associated with political priorities which are important elements in the drive for value. To put this into perspective, Hedman, et. al.
[9] discusses a business model framework for public private partnership called the 3P Framework. Society requires public and private organizations to collaborate in solving many of the world’s problems. Collaboration between public and private organizations is not easy with one of the main inhibitors being the underlying business models and underlying strategies. Hedman, et. al. indicates that one of the key problems in collaborative efforts is revenue and cost allocation. Figure 1. below presents that 3P Business Model Framework developed by Hedman, et. al.
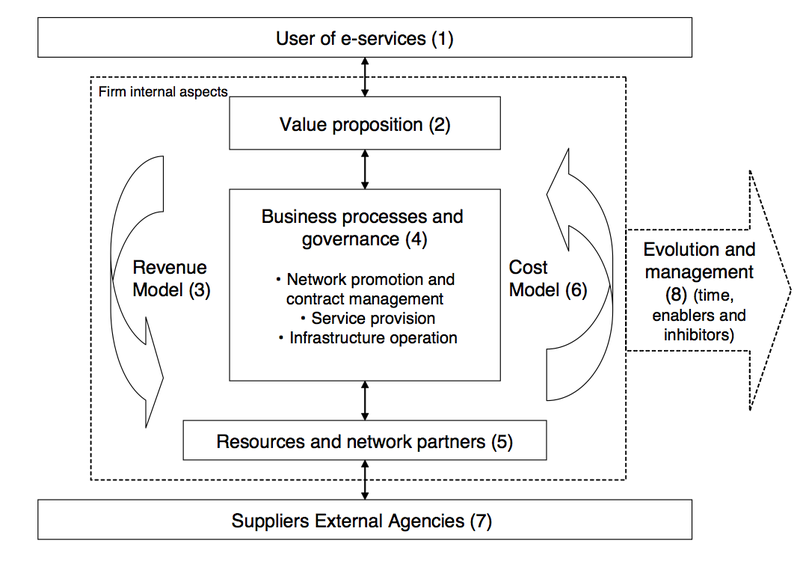 Figure 1. The Public Private Partnership (3P) Business Model Framework (from Hedman, et. al.)
Figure 1. The Public Private Partnership (3P) Business Model Framework (from Hedman, et. al.)
Briefly, the parts to this model (by example) are described as follows:
1. The user of e-services captures the competitive space or the market with users and alternative offerings or distribution channels.
2. Value proposition is often referred to as the offering where its theoretical roots are the generic strategies of differentiation and cost leadership. Offerings are usually a bundling of services or products.
3. The revenue model describes how an organization creates value for itself.
4. Business processes and organization structure or governance addresses the activities performed to acquire and transform resources into value propositions and deliver it to users.
5. Resources and network partners address vital resources of the partnership. There is a causal link between resources, business processes and value propositions. Value is ultimately determined by how well the resource improves cost or price (or customer perceived quality).
6. The cost model defines the drivers of cost. Generic drivers of cost and value include scale, capacity, utilization, linkage, interrelationships, vertical integration, local, timing, learning, policy decisions and government regulations.
7. Suppliers and external agencies address an organization’s acquisition of its inputs (resources) such as labor, raw material and financial capital. Policy makers and legal bodies are influential entities that both set the rules and control the market.
8. Evolution and management relate to the fact that business models evolve over time and must be managed and continually improved.
Public-private partnerships have the potential to: 1) assist in the initiation of public open data programs where the cost to start is prohibitive to the government organization, 2) sustain public data initiatives in the absence of appropriate government funding, and 3) provide better quality of service and lifecycle processes.
Various cost models have been discussed in research addressing the model options that a government might have in making open data available to the public. Pollock[10] discussed the economics of public sector information and public sector information holders (PSIH) and the two-sided nature of the PSIH. A PSIH is a government entity as defined in this study. Any information holder (refer to the Stakeholder discussion above) can be seen as having two sides to their operation: 1) the input (write/update) and the output (read/use) side. A government entity seeking to fund the production and maintenance of datasets has three possible options for a cost model and may not be mutually exclusive:
1. Government funding - fund from general government revenues
2. Updater funding - charge those who make changes to the dataset(s)
3. User funding - charge those who use the dataset(s)
Which of these should be used (note that option 2 is normally not an option but may be depending on the individual circumstances surrounding a dataset) will depend on the social, technological and political circumstances. Options 1 and 3 are always available but there may be cases where option 2 is feasible. These funding sources translate into charging policies, that is, the prices charged to external users and updaters. There are three basic charging policies to choose from:
1. Profit-Maximizing - Setting prices to maximize profit given the demand for the information where the assumption is that the PSIH will be more than fully funded from its revenues and so will not require any direct government funding. If the PSIH were a public sector organization the PSIH would return any profits it makes to the government.
2. Average-Cost or Cost-Recovery - Setting prices equal to the long term fixed costs relating to data production. Similar to profit maximizing it is assumed that the PSIH would not require direct government funding.
3. Margin-Cost (Zero-Cost) - Setting prices equal to the short-term marginal cost, i.e., the cost of supplying data to an extra user. With respect to digital data, this cost is essentially zero and marginal cost and zero cost pricing are identical. In this case, the PSIH’s revenues from maintaining and supplying information will fall below its costs and the PSIH will depend on direct government funding (or a subsidy) to continue its information operations.
In the profit maximizing and average-cost/cost-recovery model, strong control would be retained over the reuse and redistribution of the data while in the Margin-Cost of Zero-Cost no conditions on the reuse and redistribution of the data would be imposed.
The impact of data use based on these models may have a profound effect on the potential use of the data when it is “for-fee” or “for free”. If making government data open to the public is thought of like a utility, for example a water distribution system, usage or service fees are required to pay for the capital cost of infrastructure updates and operations costs. The same argument could be used for implementing user fees for access to public data. The quality of service depends on the ability to fund the delivery of public open data. It may be the case, however, that imposing user fees reduces the actual usage of data made available thereby reducing the business value of doing so. In the case of a margin-cost or zero-cost model, where the delivery of open data depends on the government subsidizing the effort, quality of service may be affected due to funding limitations. On the other hand, making public data available for no cost would likely result in more stakeholders using public open data. In either case, the value to the government entity is not realized directly from the process of making data available but indirectly through new value that is created as a result of making data open and accessible.
The two most common business models that will be used are: 1) profit-maximizing and 2) margin-cost (or zero cost). In the profit-maximizing business model, access to publicly available data would be available at a cost to the user. The cost structure (e.g., subscription, volume, type, etc.) is not addressed here but would be appropriate structures to evaluate if this were the chosen business model). This type of model is appropriate in a public-private partnership scenario since the user fees would be used to support the investment in the resources, technology and infrastructure required to support a public open data portal from a lifecycle perspective. In this case, the private entity would be a corporate entity that is in business to develop, deliver, manage and maintain an open data portal (the technical requirements for such a portal are significant and are discussed in a later section). The government would benefit from this type of relationship since the initial investment in the public data portal would be borne by the stockholders of the private entity. As part of the cost structure, the government may pay fees for: 1) usage of the portal, 2) feedback of usage metrics for both business and technical purposes and 3) maintenance, management and continual improvement of the consumer experience for accessing public data.
In the margin-cost or zero cost model, the government would have complete responsibility for funding the resources, technology and infrastructure required to make government open data available to public consumers. The entire financial support for the initiative would be borne by the government and there would be no user fees required for access to the data. An obvious modification of this method would be to charge from some data and not others. This is likely to be a controversial issue as the public consumers would be the judge of whether the data that they wish to access has more value (and they are willing to pay for it) than other data that is freely available.
Summary: Creating an open data system requires resources that may be a challenge for a government to be able to provide alone, and the risks associated with making public data available must be mitigated as much as possible. There are a variety of business models beyond government appropriation that should be considered.
Data
Data is the core of a progressive process to information, knowledge and wisdom. Assigning a context to data creates information. Information is the basis for gaining knowledge and knowledge is the foundation of wisdom. Data is collected and analyzed to create information suitable for making decisions. Knowledge results from experience with many different types of information on a particular subject. It is not surprising that one of the value propositions of public open data is the expansion of networks for knowledge creation.
The process of choosing what data to make available and how to deliver it is a significant part of the planning process for making data available to public consumers. While the first step is to determine the data policy guidelines, the second step is to determine how to make the data available for consumption by the public. Data policy guidelines and public dataset types (static or dynamic) are two issues that need to be addressed and assessed before making public data available for public consumption.
6.1 Data Policy Guidelines
What data should be made available for public consumption? Open data policy guidelines have been developed by the Sunlight Foundation[11] that address generally the policy and procedures for deterring what data should be made available to the public. They have outlined seven areas to address to inventory and decide on what data will be made available from the government entity. These steps include the following:
1. Proactively release government information online
2. Reference and build on existing public accountability and access policies
3. Build on the values, goals and mission of the community and government
4. Create a public, comprehensive list of all information holdings
5. Specify methods of determining prioritization of data release
6. Stipulate that provisions apply to contractors or quasi-governmental agencies
7. Appropriately safeguard sensitive information
It is important to note that making public data available to the public is a process that takes time and must be managed because it is a continual process. Publishing data that the public requests is a reactive process and likely will not yield the value results that may be realized from making open data available. Publishing data should be a proactive process and should be determined from reviews of the data inventory by the appropriate public data stakeholders and selecting datasets that are perceived to add to the generation of business value or of interest in promoting transparency.
6.2 Public Data Categories
There are two types of public data categories categorized as static and dynamic. Static data categories are those datasets that are delivered as files such as CSV or XLS (Excel files and is characterized as information that is provided to the consumer in the form of a file.
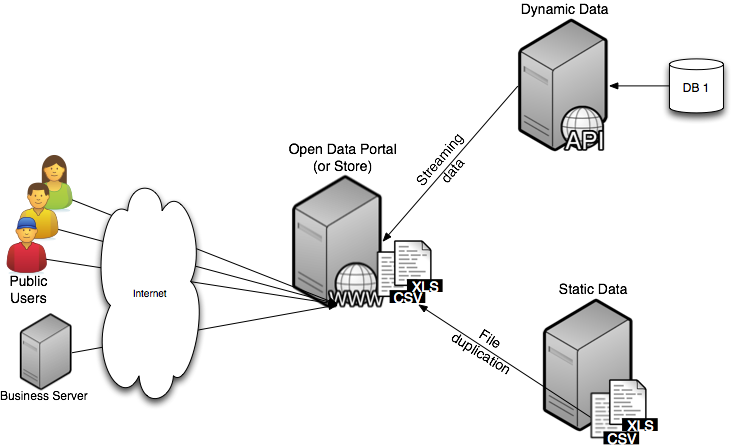 Figure 2. Static and Dynamic Public Open Data
Figure 2. Static and Dynamic Public Open Data
The file datasets in many cases are duplicated on the open data portal so that they can be accessed by public consumers (both commercial and individual users). These datasets typically require a manual process by the publisher to collect, update and publish the data, both locally and to the data portal. Data synchronization can be an issue, especially if the publisher to update the data whenever a file changes or new file becomes available does not use automated methods. Dynamic data categories are those datasets that are associated with a “service” endpoint and allow a data consumer to make requests directly to the service endpoint to receive data. The format of this data is normally in JSON or XML format. Publishing data in this manner results in lower resource requirements and does not need suffer from data synchronization problems since it is published directly from the data source.
Summary: Decisions must be made about what data should be made available, to whom, and in what format. Open data policy guidelines exist to help governments go through the decision-making process required to create an open data system.
Governance
The importance of governance in a large public ecosystem where providers and consumers interact on a continual basis, in an enterprise fashion, cannot be overemphasized. When a consumer stakeholder (public, government or business) selects a dataset to use as part of a service or product, they will expect that the data: 1) is sanctioned, 2) is managed, 3) is documented, and 4) is available. There are also policies and procedures that may be associated with supporting datasets for public use that need to be documented and followed. There is a lifecycle process on the data provider’s side associated with making data available to the public in order to ensure that sophisticated stakeholders (such as those that may develop products around certain public data) will be assured of the quality of service and availability of the data. Because there will be companies implementing different business models that will make use of the data, the data provider will need to make the appropriate assurances that the data will continue to be available and the systems making such data available will be supported.
Data accessibility needs to be managed through an enterprise governance process is. The process of providing the data is known as a service (or data service). There are different governance types that are involved; however, the primary governance process that is important to making data available to the public is IT governance. IT Governance is broken down into two areas: 1) design-time governance, and 2) runtime governance. Design-time governance includes service creation and service employment while runtime governance includes service usage and service operation. Collectively, runtime and design-time governance area necessary in order to: 1) assure data consumers that the data about to be used or being used is sanctioned, managed, documented and available. Runtime governance provides both consumers and providers information on who is using data services and how are they performing. Design-time governance assures that the data services being made available are controlled under a lifecycle process and a set of design-time policies are used to implement service interfaces to the data.
Public consumers are already using existing datasets or data services. However, it is likely that the data being used is not under any specific governance process or rules that govern how the service is to be used. Some types of runtime rules that are part of runtime governance include:
1. Access control - authentication and authorization
2. Encryption
3. Digital signatures
4. Data filtering
5. Logging
6. Statistics gathering
• Invocation rate
• Response times
All of this is part of the service lifecycle process, which includes the following:
1. Architecture - modify the service architecture to make provision for policy enforcement
2. Design - design the manner in which the rule will be implemented
3. Implement/Test - implement and test the rule
4. Deploy - deploy the revised service (which may be disruptive)
5. Operate - service enforces the rule
Enforcing policies within a service is expensive if it is not considered early in the stages of making services available and is a compelling reason to make sure that governance processes are used around public open data provided by government providers.
Design-time governance represents the rules that bind the way that a dataset or data service is provided to the public. Existing services already being provided to the public should be included in a governance repository in order to assure that existing services are being delivered with the same quality of service as new data services that are implemented over time. Considerations during the design phase of creating a data service include:
1. Architecture
• Will the service fit multiple usages?
• Will the interface remain stable over time?
2. Implement/Test
• Is the testing adequate?
• Is the documentation adequate?
3. Operate
• Manage service operation (start/stop)
• Manage service versioning
From a solution lifecycle perspective, design-time issues that should be addressed include:
1. Architecture
• Are existing services being used?
• Are new services being built appropriately?
2. Implement/Test and Deploy
• Has service capacity planning been done?
• Have policies been put in place for service access?
3. Operate
• Coordinate with service operation
• Track service versioning
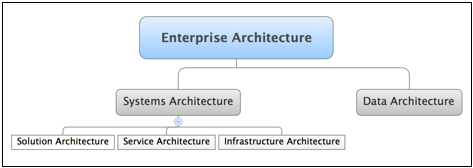 Figure 3. Design-time Governance and Enterprise Architecture
Governance is a critical part of successfully delivering open data to public consumers. The process of governance could be used as a differentiator of the government entity providing the data versus other similar government entities. The process of delivering public data is as valuable to the consumer of public data as the data itself.
Figure 3. Design-time Governance and Enterprise Architecture
Governance is a critical part of successfully delivering open data to public consumers. The process of governance could be used as a differentiator of the government entity providing the data versus other similar government entities. The process of delivering public data is as valuable to the consumer of public data as the data itself.
The scope of the Enterprise Architecture process should be to:
1. Evaluate service opportunities
• participate in service specification
2. Provide technical coordination between projects
3. Provide look-ahead technical guidance for future projects
Architecture and data service projects should be combined under a common organization. See Figure 4. for an organization structure to manage the delivery of public data to public data consumers and that enforces design-time and runtime governance.
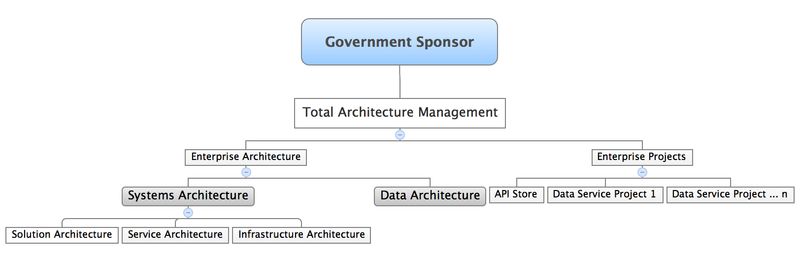 Figure 4. Organizational Structure for Managing the Delivery of Public Open Data
Figure 4. Organizational Structure for Managing the Delivery of Public Open Data
Summary: Users expect data to be sanctioned, managed, documented, and available; policies and procedures are needed to ensure that these expectations are met. Data services provided in the system need to consider system architecture, design, implementation, and operation to meet the needs of both publishers and users.
Legal
Several researchers have reviewed licensing public data for use. Open data licenses that potentially have applicability for personal and commercial use of open data is listed in the following table[12].

Table 2. License Types for Public Data Usage (from Korn and Oppenheim)
The type of license will depend on the business model used for delivering open data to the public. For example, a Profit-Maximizing business model would require a license that does not allow the user to make it available for re-use. License type selection will be dependent on how the data is made available to the public and the restrictions on re-use. Careful consideration of the source of data is important as some government entities may determine that a fee should be paid to allow access to such data. In that case, re-distribution of the information is now allowed and needs to be carefully assessed for each dataset that is made available for public consumption.
Summary: There are many types of licenses used for data, both public and private. The source of the data, legal constraints on re-distribution of data, and data privacy concerns must all be considered carefully.
Risk
Opening up public data is the result of a political commitment[13] that raises risks related to the objectives and the sustainability of the initiative. Risks associated with governance, economic, license and legal frameworks, data, metadata, access, and user and re-user skills from Martin, et. al., in a study about the experiences of Rennes in France, Berlin in Germany and the United Kingdom, are presented in the following table:
 Table 3. Risk Analysis to Overcome Barriers to Open Data (from Martin, et. al.)
Table 3. Risk Analysis to Overcome Barriers to Open Data (from Martin, et. al.)
Summary: There are risks associated with many aspects of an open data system to consider. These risks can be related to the data itself, metadata that provides information about data, access to the data, users of the data and their skills, licenses and legal frameworks in which the data exist, or governance of the data.
Financial
Delivering government open data to the public must be managed and will require additional computer software and hardware resources to manage it. Since there is no quantifiable way to determine a return on investment (e.g., how does one measure the financial benefit of transparency, or how does one predict the increased economic value as a result of making open data available), the question arises as to what are the financial implications (that is, what does it cost), to get started on making public data available. More importantly, is there value to centralizing access to all government entity data (e.g., a city or state), so that users of public open data know that all datasets described are the known, available data provided by the government entity? As important as knowing what data is available, the data is documented and supported reducing the risk on the user that the data is sanctioned and supported.
There are two types of costs that must be evaluated: 1) the costs associated with providing a portal where all datasets provided by the government entity are monitored and managed, and 2) the costs of exposing new and supporting existing datasets. In both cases, the entire ecosystem needs to be managed so there is a resource cost to monitor, manage and maintain the systems that are used to deliver the public data.
Investment costs must be determined in order to quantify the financial aspects of opening up government data. Functionality that should be included in a centralized portal includes:
1. Searchable portal
2. Inventory of existing datasets and API’s
3. Monitoring usage of datasets and API’s
4. Governance of datasets and API’s
These general functional needs must be interpreted into a solution architecture that addresses the application, technical and information requirements for the public data ecosystem.
The costs need to be identified and determined when engaging on a project to make open data available. In general, the costs that need to be identified include the human resources to plan, design, implement and deploy a portal system and the technology requirements. Once datasets are made available to the public, they must be governed in order to ensure users that the data is sanctioned and managed. From an IT perspective, that means putting the dataset into a lifecycle management process, where continual service improvement will assure that users are satisfied with the quality of data and the performance that it is provided. The first step, however, is to determine what data should be made available to the public. The second step, once a dataset is made available to the public, is to continually update the data and refine the implementation as dataset usage increases. Datasets made available should be governed using a lifecycle process where monitored information on dataset usage is used to continually determine what datasets are being used and where performance issues are impacting the usage of the dataset. Providing a holistic view of the open data ecosystem is critically important to the success of the implementation.
The initial investment required to develop and deliver a public data ecosystem does not yield a return on investment (ROI) that can be quantified since there is no quantifiable way to measure value. For example, what is the value of increased economic activity resulting from making public datasets available? Initial investments will be important since minimal investments will yield minimal results. In many cases, existing datasets are already being made available but not in a centralized manner. For these situations, the initial investment in a centralized portal should, at a minimum, include these existing datasets resulting in a way to begin to measure the usage of such datasets and by whom. This type of information will serve to provide analytics that may be useful in projecting the value of making other datasets available to the public. Internal usage of datasets by the governmental entity should not be overlooked in this process as information from different departments can be combined to create new applications that: 1) reduce development costs within a department, and 2) create more visibility to value of cross-departmental applications.
In order to measure the value of making open data available to public users (individuals and businesses), information needs to be collected to understand “who” is using “what” data. While this would seem to be counter intuitive to making data freely available to anyone without knowledge of who the entity using the data is or how they might be using it, it is a necessary requirement of the public data ecosystem to make sure that both publishers and consumers gain value from making the data available for public use. In order to measure the potential value of public data usage, it must be monitored. To that end, to measure the financial impact to the government entity providing the data, and assurance that data will continue to be made available to users of the quality and performance that they need to continue using it, monitoring of public data usage is required. While it may seem to be invasive to the user of public data to monitor who is using public data and how it might be used, a government entity cannot justify making investments in the backend and portal systems if there is no clear benefit to the public consisting of individual and business consumers. To that extent, anonymizing users of public data can be accomplished in order to assign usage patterns to a general group of businesses or individual users.
Summary: Two types of costs should be considered when planning an open data system: costs associated with providing and monitoring an open data portal as well as costs associated with adding new data sets and supporting existing data sets.
Open Data Ecosystem
Most efforts at making public data available to users has gotten started through creating local hackathons where a group of civic-minded people get together to determine what data is made available to address a particular civic problem they are working on. This in turn has led to the need to inventory this data through the use of some type of data portal. In many cases, vendors such as Socrata or Junera provide starter systems where a certain number of datasets are made available at no cost for public access. While this has been a good measure of the interest of public citizens in the use of using government data to solve civic problems, it has the danger of becoming an unmanaged, uncontrolled process. Even with a way to centralize and categorize data at a portal location, there are no assurances that the data available is supported from a governance and lifecycle perspective. Without the assurances of the quality of the data and future support of the dataset availability, users are at significant risk to use the data, especially if commercial applications begin to materialize as a result of using the data.
A broader view of the publication and consumption of open government data needs to be addressed. The publishers are the data owners within the government entity that make the data available for use. The consumers are the individual and business users who determine that the availability of data to address a particular problem is of value to them for their use. This suggests that a centralized location needs to be created that will connect the publishers and subscribers in meaningful ways (a subscribe wants to know the dataset is supported while a publisher wants to know how the dataset may be used). The centralization of this information is of value to both publishers and subscribers to information. On the publisher side, however, there needs to be lifecycle processes and governance (design-time and runtime) processes that are required to required to make the assurances to consumers about the data being used. It is not so simple as to provide a user an endpoint to an API. There needs to be a lifecycle approach to making data available that may include: 1) strategy, 2) design, 3) implementation, 4) operation and 5) continued improvement. Only then can assurances be made to subscribers about the quality of the data and the quality of service provided for access to the data.
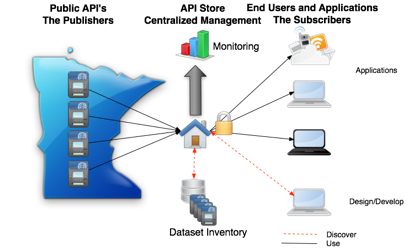 Figure 5. Conceptual Solution Architecture for Public Data Ecosystem
Figure 5. Conceptual Solution Architecture for Public Data Ecosystem
The public data ecosystem is shown conceptually in Figure 5. The central portal including monitoring and dataset inventory functions is key component of the public data ecosystem and forces appropriate governance processes and monitoring processes to ensure visibility to the business value of making public data available.
Summary: A broad view of publication and consumption of data is needed to ensure that high-quality data is provided in a managed and supported way. A lifecycle approach to strategy, design, implementation, operation, and continued improvement of data will maximize benefits captured from an open data system.
Ecosystem Requirements
The determination of ecosystem requirements is based on a number of the functions that need to be provided to assure consumers of public open data of the quality of data and the quality of service provided. More importantly, it promotes the usage of the data because of the processes and technology that are used behind making public data available. In general, there are four major system requirements that must be addressed. These are:
1. Governance of datasets that are categorized as static or dynamic
- design-time
- runtime
2. A centralized portal that presents and documents (catalogs) all of the datasets that are available from the government entity (static and dynamic)
3. Static and dynamic usage monitoring
4. Transformation of static datasets
These ecosystem requirements are high level and need to be broken down into the details of classical enterprise architecture processes such as determining “what” needs to be done (a business view) and “how” it needs to be implemented (a technical view). This information will be expanded in other documents that address each of these views in more detail.
Summary: Consumers of data need to be sure of access to quality data and quality of service, and publishers need to have a better understanding of how their data is used and how consumers want it provided to them. Determining the requirements of the open data ecosystem is a process that should involve diverse stakeholders to identify the functionality needed to create a robust system that works for all.
References
[1] McKinsey Global Institute, “How Government can Promote Open Data and Help Unleash over $3 Trillion in Economic Value”, Government Designed for New Times, 2013.
[2] McKinsey Global Institute, “Open data: Unlocking innovation and performance with liquid information”,http://www.mckinsey.com/insights/business_technology/open_data_unlocking_innovation_and_performance_with_liquid_information, October 2013.
[3] Howard, A., “What is the ROI of open government?”, http://gov20.govfresh.com/what-is-the-roi-of-open-government/, March 2013.
[4] Sunlight Foundation, “Open Data Guidelines”, http://sunlightfoundation.com/opendataguidelines/.
[5]McKinsey Global Institute, “The social economy: Unlocking value and productivity through social technologies”, http://www.mckinsey.com/insights/high_tech_telecoms_internet/the_social_economy, July 2012.
[6] Burwell, S.M., VanRoekel, S., Park, T., and Mancini, D.J., “M-13-13 - Memorandum for the Heads of Executive Departments and Agencies”, http://project-open-data.github.io/policy-memo/.
[7] Rowley, J., “e-Government stakeholders - Who are they and what do they want”, International Journal of Information Management 31 (2011) 53 - 62.
[8] Chircu, A.M., “E-government evaluation: Towards a multi-dimensional framework”, Electronic Government: An International Journal, 5(4), 345 - 363 (2008).
[9] Hedman, J., Lind, M., Olov, F. and Lars, M., “Business Models for Public Private Partnership: The 3P Framework”, Collaboration and Knowledge Economy, IOS Press, Amsterdam (2008).
[10] Pollock, R., “The economics of public sector information”, Cambridge University, Cambridge Working Papers in Economics, May 2009.
[11] The Sunlight Foundation - http://sunlightfoundation.com/opendataguidelines/
[12] Korn, N. and Oppenheim, C., “Licensing Open Data: A Practical Guide”, www.web2rights.com/OERIPRSupport
[13] Martin, S., et. al., “Risk Analysis to Overcome Barriers to Open Data”, Academic Publishing International, e-Journal of e-Government, Volume 11, Issue 2, December, 2013.